Ordinarily, the telecoms industry is much less associated with the theme of sustainability than many other so-called “heavy” industries such as energy, chemicals or automotive. An obvious explanation for this is that the telecoms industry is much less carbon-intensive, and consequently could be seen as greener. However, appearances can be deceptive
It is a mistake to equate “sustainability” with “green” – sustainability is more encompassing than green, comprising not only environmental issues but also social, marketplace and quality of life issues. As any telecoms executive can testify, the industry has to cope with plenty of sustainability issues, such as digital divide or inclusion, security, privacy and responsible content. Various initiatives have been undertaken in this regard, such as the Global e-Sustainability Initiative (GeSI), a partnership of information & communication technologies (ICT) companies that promotes technologies for a sustainable development.
Telecoms players are also well positioned to help other industries cope with sustainability challenges. Telecoms provide not only a medium of communication but also function as an enabler for several customer industries, including healthcare, education, public services, transportation, building, and agriculture – particularly within developing economies.
In this article, we will provide a brief perspective on how to address these two questions:
How can telecoms companies tackle their own sustainability challenges?
How can telecoms companies enable and enhance the sustainability of other industries, and thus open up new market space for their own products and services?
Tackling telecoms’ own sustainability challenge
Sustainability issues in the telecoms industry have four common drivers:
Reduction of operational expenditure – as the operation of a mobile network is a significantly energy-intensive process, a large percentage of the OPEX for a telecoms operator is sunk into the energy cost of running the transmission network; a
projected rise in energy costs leaves these operators exposed to higher energy prices and reduced margin
Rapidly evolving legislation and regulation – while the ICT industry has thus far largely avoided environmental scrutiny, legislation and regulation are evolving quickly to bring the industry on par with other energy intensive industries
Product creation and revenue development – Swiftly evolving technology and historically fast churn are beginning to compete with consumer attitudes towards sustainability; ICTs are looking for alternative streams of revenue and clever business models to address sustainability issues
Consumer preferences and predominance of the social dimension – Lifestyles of Health and Sustainability (LOHAS) consumers are pushing manufacturers and service providers to offer a broader portfolio of sustainable products. In a recent Arthur D. Little consumer survey, more than 50 per cent of the respondents indicated that a greater availability of green products would increase their overall purchases of green goods. Understanding these drivers is essential to managing and coping with sustainability issues in a strategic manner. A strategic approach to sustainability focuses on what a company can do in order to convert risk into opportunity, rather than simply managing or avoiding risk. Telecoms companies must shift from a risk-driven to an opportunity-driven approach.
Enabling sustainability in other industries 
Telecoms has a powerful role to play in enabling and enhancing the sustainability of other industries. Through the provision of new products and services, or the innovative application of existing ones, telecoms companies can support firms in other industries transform sustainability issues into new sources of revenues and competitive advantages, while at the same time providing benefits to the recipient industry, society and the environment.
A four-step approach has been established to support telecoms companies in identifying and realising these opportunities:
Step 1: Select the most promising target industries. An ICT company’s adjacent industries often offer opportunities for technology innovation both at product or process level; identifying a match between another industry’s ICT needs and
one’s own knowledge base and capabilities will help deliver sustainable technological innovation.
Step 2: Identify the target industry’s most relevant sustainability issues. Sustainability issues within the target industry must be identified, analysed and prioritised in terms of relevance and business impact. After the most relevant sustainability issues have been prioritised, it can be determined what opportunities exist for telecoms to best address these issues – either through the innovative use of existing products/services or through the development of new products and services.
Step 3: Analyse and prioritise opportunities. Criteria must then be established for screening and ranking identified opportunities. “Attractiveness” versus “feasibility” is a good starting point in assessing the match between targeted opportunities and a telecoms company’s capability to implement adequate solutions. By applying the criteria, a shortlist of opportunities is then established.
Step 4: Select the opportunities that maximise the mutual benefits for all stakeholders.
This step selects those opportunities that will have mutual benefits for the telecoms sector, the targeted industry, the environment and society. Obviously, the nature of the benefits will vary based on the stakeholder, but through quantifying the potential benefits, business cases can be prepared and opportunities selected that will maximise the potential impact.
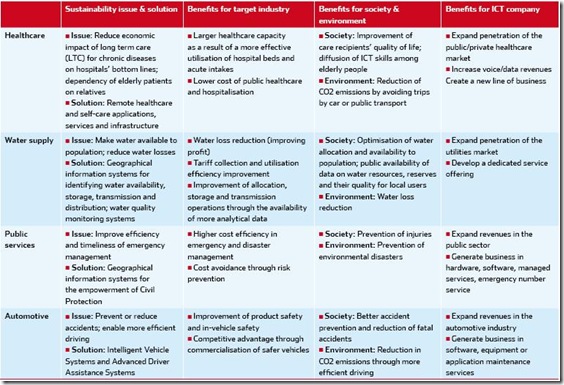
Examples of ICT-driven solutions in other industries:
It is no surprise that within the healthcare industry, the demand for ICT-enabled solutions is strong. The application of ICT can make the healthcare system more efficient by reducing the trade-off between quality and cost of service. Many European countries have collaborated to establish an “eHealth Plan”, aimed at supporting national health systems in reducing treatment costs and enhancing treatment quality.
Summary
Consumers attribute increasing value to the environmental and social performance of products and services and, consequently, to the companies that produce them. Consumer preference is increasingly being driven by environmental friendly and responsible lifestyle and consumption attitudes. Likewise, investors are directing their monies with an eye on the value of sustainability.
The telecoms sector has a profitable opportunity and is in a strong position to impact sustainability on two levels: by addressing the sustainability issues within its own industry, and functioning as a vehicle to support other industries in coping with their own sustainability challenges. Telecoms companies should shift from a risk-driven to an opportunity-driven approach, that is, move from a defensiveness and compliance stage to a strategic one by reframing social and environmental issues not as risks, but rather as sizeable and tangible market opportunities. By doing so, optimising corporate performance and sustainability is not a zero-sum game – both the company and society can win.
This article was contributed by Zoran Vasiljev, director of Arthur D. Little, Middle East & South East Asia





0 comments ↓
There are no comments yet...Kick things off by filling out the form below.
Leave a Comment